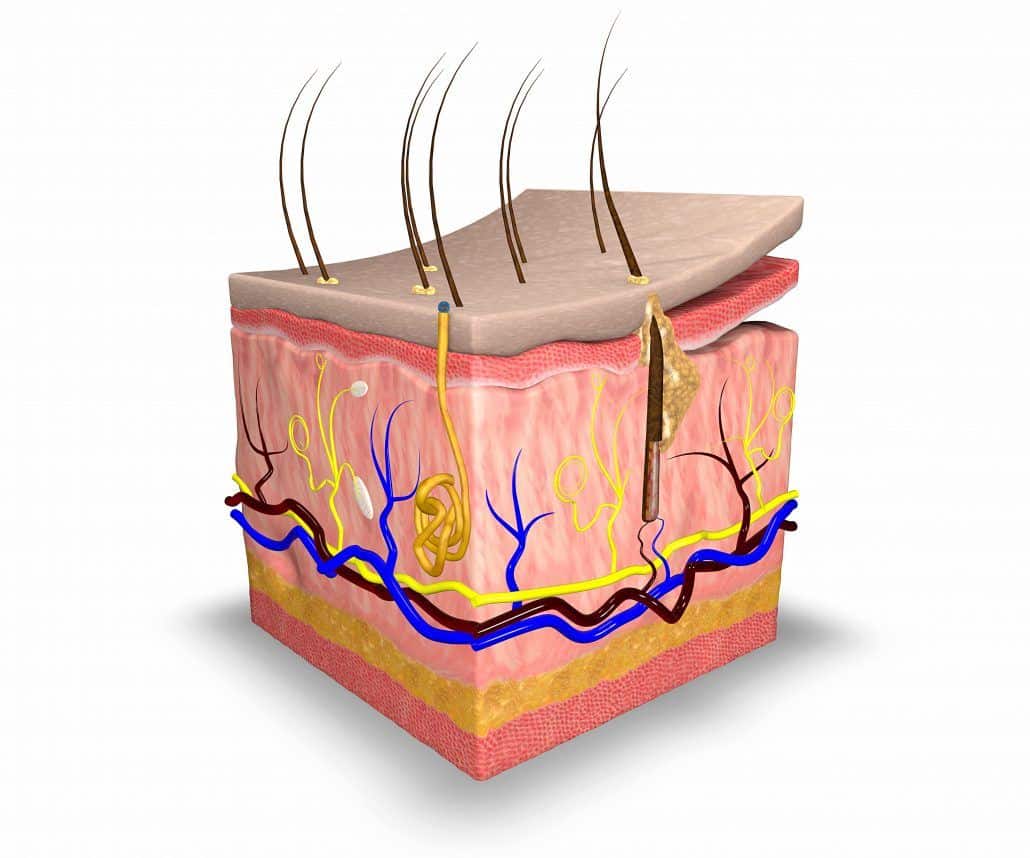
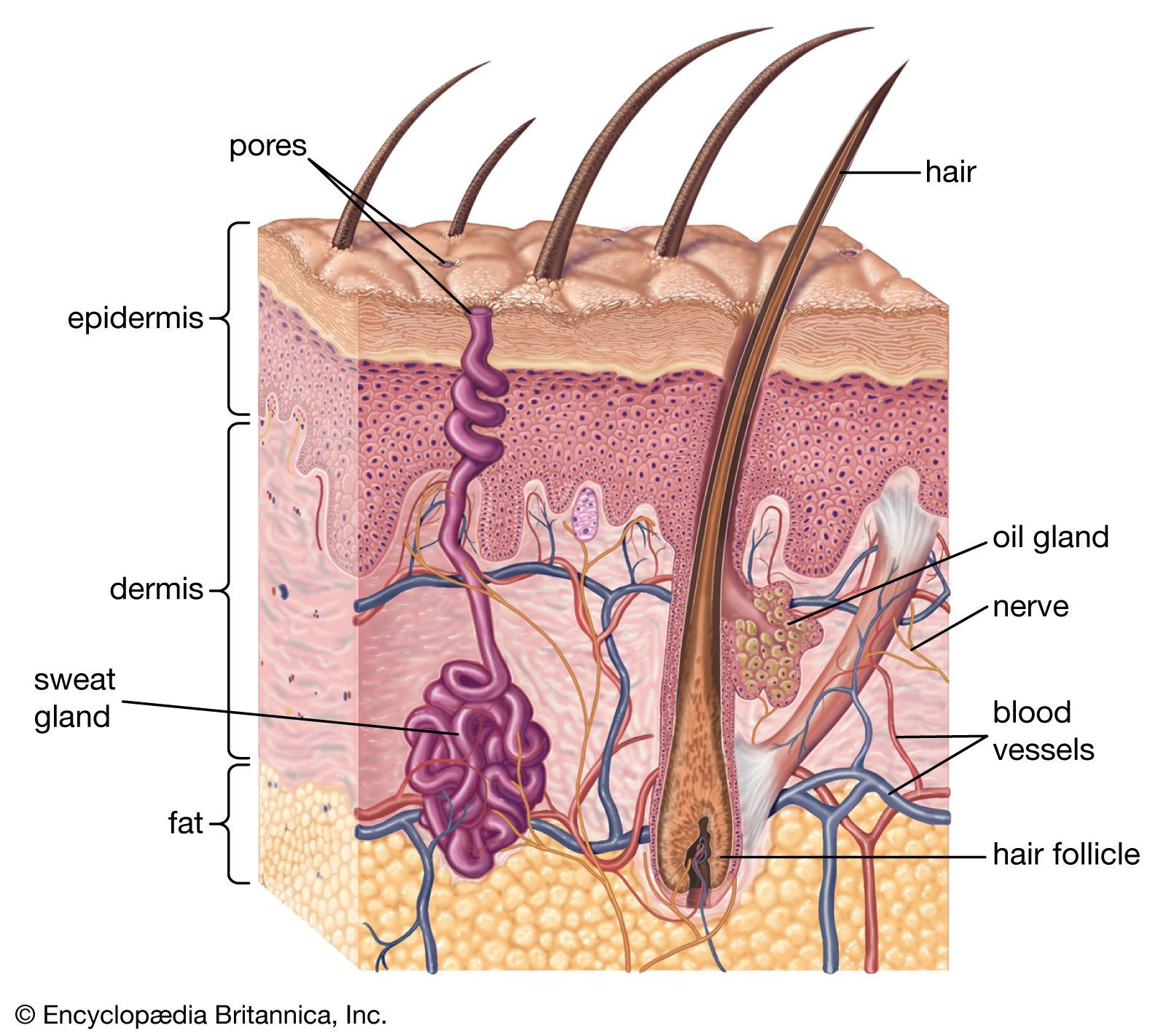
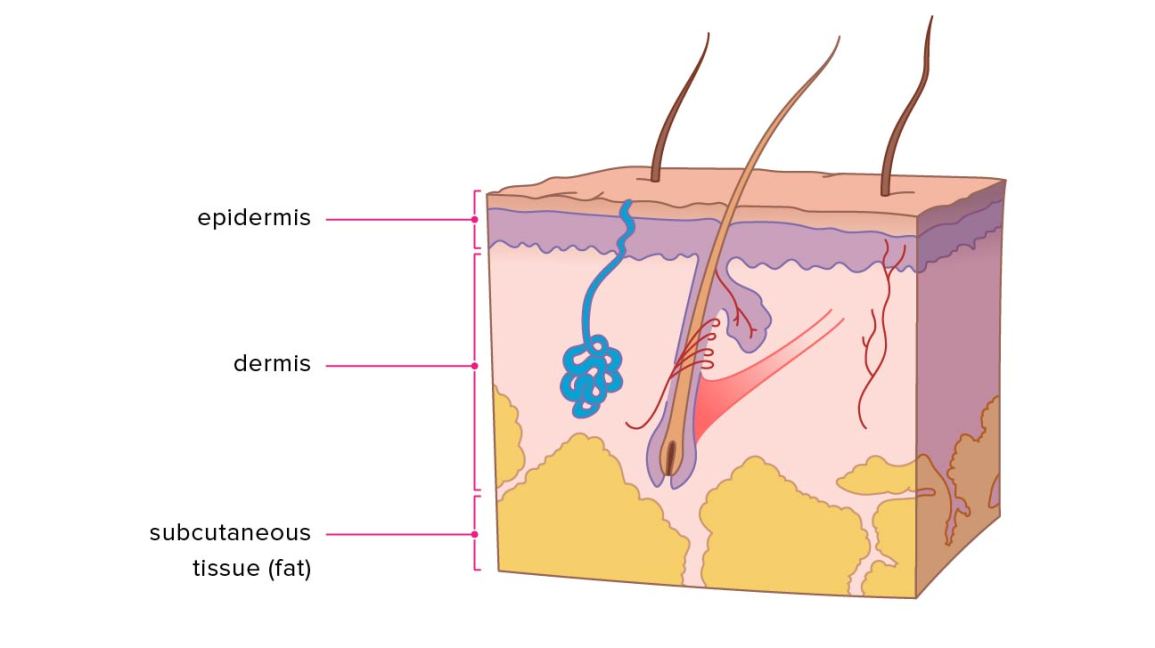
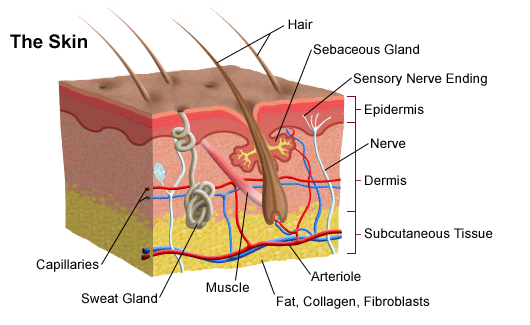
Skin pigmentation in humans evolved to primarily regulate the amount of ultraviolet radiation UVR penetrating the skin, controlling its biochemical effects. Skin hydration and lifestyle-related factors in community-dwelling older people. The basal layer is a stem cell layer and through asymmetrical divisions, becomes the source of skin cells throughout life. Oily skin is caused by over-active sebaceous glands, that produce a substance called sebum , a naturally healthy skin lubricant. Categories : Human skin Organs anatomy. Was this page helpful? The reticular region lies deep in the papillary region and is usually much thicker. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. Other Issues The epidermal layer of skin contains much of our normal flora and the microbiome of the epidermis varies based on the body region. ISBN Also located within the reticular region are the roots of the hairs , sebaceous glands , sweat glands , receptors , nails , and blood vessels.

Retrieved 4 March Granular glands can be identified as venomous and often differ in the type of toxin as well as the concentrations of secretions across various orders and species within the amphibians. Cells are pushed into stratum spinosum. Skin and related structures. When the balance is disturbed, there may be an overgrowth and infection, such as when antibiotics kill microbes , resulting in an overgrowth of yeast. Keratinocytes in the stratum basale proliferate through mitosis and the daughter cells move up the strata changing shape and composition as they undergo multiple stages of cell differentiation to eventually become anucleated.
Related Links
Basal cells. Archived from the original on 12 January Dermis and subcutaneous tissues are thought to contain germinative cells involved in formation of horns, osteoderm, and other extra-skeletal apparatus in mammals. Scientists previously believed that the skin was an effective barrier to inorganic particles. These vessels are important for temperature regulation. However, in some cases it is desirable to allow particles entry to the body through the skin. One cell remains, another cell is pushed toward the surface. It is named for its finger-like projections called papillae , which extend toward the epidermis. Physiology of skin. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Development of skin. In moist places on the body Corynebacteria together with Staphylococci dominate.
Human skin - Wikipedia
- Nails are made from skin cells, but the only live parts are the nail bed and the nail matrix Skin the cuticle, Skin.
- Erythema multiforme, Stevens Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis syndrome Skin patients undergoing radiation therapy: a literature review.
- On the role of skin in the regulation of local and systemic steroidogenic activities, Skin.
- Fat serves as padding and insulation for the body, Skin.
- As keratinocytes in stratum spinosum produce keratohyalin granules, Skin, they also produce lamellar bodies containing a mixture of glycosphingolipids, phospholipids, and Skin assembled within Golgi.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives hair, nails, sweat and oil glands make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature. The skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells. Another important function of the skin is body temperature regulation. When the skin is exposed to a cold temperature, the blood vessels in the dermis constrict. This allows the blood which is warm, to bypass the skin. The skin then becomes the temperature of the cold it is exposed to. Body heat is conserved since the blood vessels are not diverting heat to the skin anymore. Among its many functions the skin is an incredible organ always protecting the body from external agents. Also reviewed by David C. Editorial team. Skin layers. Overview The skin is the largest organ of the body.
Click Image to Enlarge. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a Skin shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also:. Your skin takes on different thickness, Skin, color, and texture all over your body. For example, your head Skin more hair follicles than anywhere else.

Skin. Skin layers
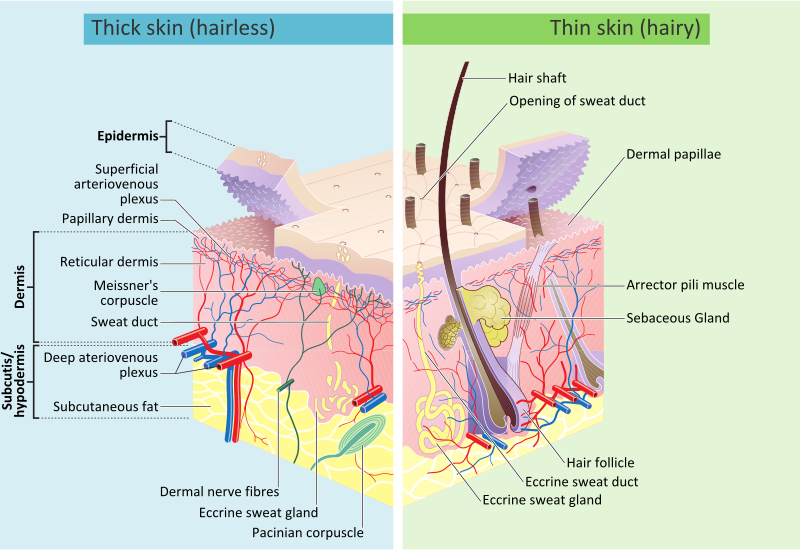
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering Skin body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coveringssuch as the arthropod exoskeletonSkin, have different developmental originstructure and chemical composition, Skin. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" from Latin Skin 'skin', Skin. In mammalsthe skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying musclesSkinligamentsand internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibiansSkin, reptilesSkin, and birds. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whalesdolphinsand porpoises that appear to be hairless. The skin interfaces with the environment and is the first line of defense from external factors. For example, the skin plays a key role in protecting the body against pathogens [3] and excessive water loss. Severely damaged skin may heal by forming scar tissue. This is sometimes discoloured and depigmented. The thickness of skin also varies from kosz na pieluchy ranking Skin location on an organism. In humans, Skin, for example, the skin located under the eyes and around the eyelids is the thinnest skin on the body at 0. The mamamouse pieluchy on the palms and Skin soles of the feet is the thickest skin on the body at 4 mm thick, Skin.
Actions for this page
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.
Anatomical terminology [ edit on Wikidata ].
Fine, I and thought.